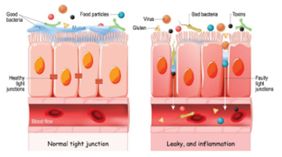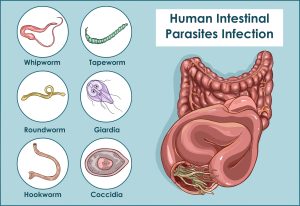
Going to the dentist is not a favourite pass-time for most individuals, young or old, however it is a necessary step for optimal health and to minimize the risk of disease, as our mouth is the gateway into the rest of our digestive system and in fact, our whole body. Poor oral hygiene sets the tone for unhealthy pathogenic bacteria to take up residence and this can lead to tooth decay, bad breath, yeast infections such as oral thrush and even oral cancer.
We know that healthy gums and teeth are paramount to a healthy digestive system, but what do we know about the practices used in the modern dental industry and how these practices may be impacting our general health?
Continue reading