What is the definition of Leaky Gut?
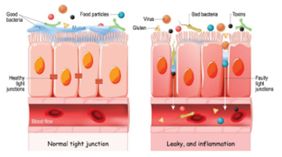
Intestinal permeability refers to how easily substances pass through the intestinal wall, and when there is a high amount of inflammation, the otherwise tight junctions of the intestinal walls become loose, making it more permeable. This allows food particles, bacteria, or toxins to leak out into the blood stream, and this is when the term “Leaky Gut” is used. When the lining of the small intestine becomes irritated and damaged, small particles of food and waste leak through the intestinal wall and into the blood stream, causing havoc all around the body. These foreign particles are identified, and this launches an immune response such as an inflammatory or allergic reaction. When this is continually happening day after day, the problem can become more serious, resulting in an autoimmune condition, where the body is constantly attacking itself.
When the gut lining is damaged and inflamed, nutrient absorption abilities dramatically reduce, leading to poor levels of iron, protein, and essential nutrients. As nutrients are needed for every single biochemical process in the body, this state of malnutrition can lead to other problems such as hormonal imbalances, a weakened immune system and chronic fatigue.
What are the symptoms?
The most common and obvious symptoms are those relating to digestive health, including pain when eating (dyspepsia), bloating, loose stools, incomplete elimination of stools, all kinds of food allergies or reactions to certain foods, headaches, skin conditions, fatigue and joint pain. Over time, joint pain can lead to arthritis or even worse, rheumatoid arthritis, which is an autoimmune condition.
As the problem tends to compound itself over time, the symptoms can extend to all kinds of skin conditions and mental health problems including behaviour disorders, depression and anxiety. This often leads to poor food choices, which compounds the problem even further.
The problem with this condition is that there are many other triggers to these sorts of symptoms, and the medical system is not very good at diagnosing or treating it, as there are no pharmaceutical solutions.
As treatment usually involves specific diets and the exclusion of inflammatory foods, doctors are generally not equipped to provide advice or solutions, as they have not had any nutrition training. The condition is also often created or exacerbated by pharmaceutical drugs including over the counter pain relievers, which irritate the intestinal lining and damage protective mucus layers. This irritation can start or continue the inflammation cycle that leads to an inflamed and permeable gut.
Diseases associated with Leaky Gut
To quote the Greek physician Hippocrates some 2,500 years ago, “All disease begins in the gut”, but some of the most common and well researched diseases linked to leaky gut include Celiac Disease, Diabetes, Crohn’s Disease, IBS, IBD and generalised food allergies. Skin conditions such as psoriasis and eczema are often dramatically improved when a quality gut healing program is used, as are all kinds of brain function conditions (anxiety, depression, Alzheimer’s, Dementia). Just about every autoimmune condition can be dramatically improved if not held into remission, when a proper gut healing protocol is used, and an anti-inflammatory diet is maintained.
What causes it?
The modern food industry has become over-industrialised, making it difficult to avoid all the causes of leaky gut, which include;
- High consumption of processed foods.
- Inflammatory diet, including wheat, dairy, alcohol and caffeine.
- Consumption of foods high in sugar and refined carbohydrates (white flour).
- GMO foods, including wheat, soy and canola.
- Consumption of products that contain Palm oil (vegetable oil) (most processed and baked goods).
- High levels of the heavy metal Cadmium, often coming from synthetic fertilizers used to grow fresh food.
- High levels of mercury, often coming from old dental amalgams that are damaged or being grinded at night.
- Chlorine from treated mains tap water or swimming pools.
- Anti-biotic use that destroys healthy bacteria along with the pathogenic bacteria.
- High levels of stress causing low stomach acid and indigestion (dyspepsia).
- Medications that lower stomach acid (PPIs) or antacid medications that neutralize the acid.
- Pain medications such as NSAID’s (ibuprofen which irritates the gut lining and aspirin which is often used daily by the elderly as a blood thinner).
- Intestinal infections such as SIBO, Parasites or Candida.
- Animal proteins that are fed anti-biotics and growth hormones.
- Low consumption of pre-biotic and probiotic foods.
How do I heal it?
Healing an inflamed gut takes several approaches. First and foremost, removing the underlying causes, whether that be inflammatory foods, drinks and medications, to give the gut a fighting chance of healing itself. Reducing stress and ensuring quality sleep also play a role in the healing process. Treating intestinal infections is also very necessary before the gut lining can truly heal.
Holistic natural health practitioners understand all the contributing factors to a leaky gut, and being under the guidance of an experienced practitioner is highly advisable. The concepts of healing however, include the following;
- Removal of all inflammatory foods including wheat, sugar, baked goods, junk foods, processed foods.
- Reduce or cease inflammatory drinks such as coffee, alcohol, soft drinks of all kinds, fruit juices unless they are freshly made and include high amounts of vegetables.
- Management of stress.
- Quality deep restorative sleep.
- Reducing medications where possible, especially those that change stomach acid levels (speak to your doctor about this).
- Quality probiotics that contain a broad spectrum of species in high quantities (not all probiotics are equal)
- Quality gut healing powder with ingredients that promote healing and repair.
- Treat underlying intestinal infections to remove pathogenic bacteria, yeasts and parasites.
- Adherence to a diet that is high in vegetables, plant-based proteins and healthy fats and small amounts of organic animal proteins.
The healing process can take at least 4-6 weeks and often longer depending on the degree of damage there is and people can often start to feel a difference after 2-4 weeks.
I’m healed, what now?
The healing of a leaky gut does not have a finish line per se. Learning how to eat in a healthful and anti-inflammatory way is how we should all be eating every day as this dramatically improves our quality of life and the risks of diseases such as autoimmune conditions, cancer, mental health, hormonal imbalances, and pain of all kinds, and who doesn’t want that? Having an abundance of energy, good mental health and being disease free, means we can enjoy life to the fullest, which creates a healthy society. Changing our relationship with food and the priorities that support managing our stress better, a healthy gut means a healthy you. Our food industry is set up for convenience and profits, not health and the more we understand and educate ourselves, the more power we have to take back our health.
